 |
AutoFEM Analysis Details of Thermal Analysis Steps | ||||||
Thermal analysis is performed in several stages. The sequence of the user's steps for putting together a study and running a thermal study of a structure is in many parts similar to algorithms of working with other study modules of AutoFEM. Therefore, we will point out in this chapter only certain details specific to thermal studies.
1. Creating Study. When creating a study, specify its type – «Termal Analysis». As in other study types, building a finite element mesh is required, for approximating the structure's geometry.
2. Applying boundary conditions. In the thermal analysis, the boundary conditions are represented by the boundary and initial temperatures, heat power sources, heat flux, and conditions of heat exchange between the model and environment – convection and radiation applied to the model.
The initial temperature is used for defining thermal loads at the initial (zero) moment of time for the transient thermal analysis only. All thermal loads defined without the «initial» flag are considered constant (invariable) in both the steady state and transient thermal analysis.
3. Solving. Before running calculations, the user can specify the type of a thermal analysis study being solved (the [Parameters] tab, steady-state or transient heat transfer), and, if necessary, adjust algorithms for solving systems of equations on the [Solve] tab.
4. Analysis of thermal solution results. The results of a thermal analysis are:
Temperature fields – temperature distribution over the model's volume.
Thermal gradients by the X, Y, Z axes, and the magnitude of the thermal gradient – reflect on the degree of temperature changes by the respective axes of the coordinate system.
Resulting thermal flux by the X, Y, Z axes, and the magnitude of the resulting thermal flux –show the rate of thermal energy transfer, determined from the solution to the thermal analysis study.
Magnitudes of the thermal (temperature) gradient and the resulting heat flux are determined as the square root of the sum of the squares of the respective coordinate-projected components.
Besides the mentioned results, the following reference data can be displayed in the postprocessor window:
•Prescribed thermal flux corresponds to the specified initial parameters of thermal loads.
•Prescribed temperature – constant thermal loads applied to the model.
•Initial temperature – the initial temperature field applied to the model (for the transient thermal analysis).
The methods for analysing results of thermal analysis accepted in the AutoFEM Postprocessor, are in general similar to the methods of examining results in other analysis modules. Let us mention some specific Postprocessor tools, which can be used for analysing results of transient heat transfer.
Solving a transient heat transfer study results in a large set of data, whose total number is equal to the number of time steps specified by the user. AutoFEM provides the user with a convenient visual interface for managing the entire array of data resulting from calculations. For this purpose, a «Time process» dialogue panel can be called from the results viewing window's context menu, that can be used by the user to quickly switch to the desired result on the time scale.
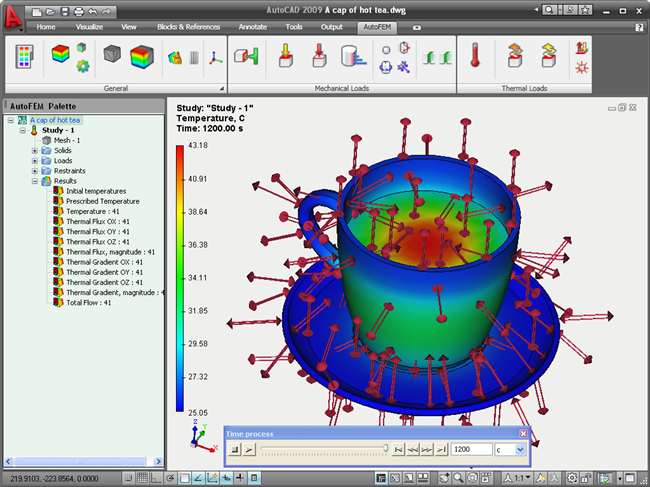
Use of the «Time process» window for managing access to the results of a transient thermal study